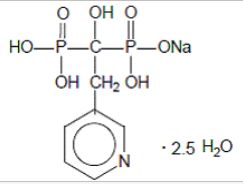
Risedronate Sodium Is The Sodium Salt Of Risedronic Acid, A Synthetic Pyridinyl Bisphosphonate. Risedronic Acid Binds To Hydroxyapatite Crystals In Bone And Inhibits Osteoclast-dependent Bone Resorption. Biphosphonate, A Salt, Ester, Or Anion Of A Dimer Of Phosphonic Acid (Diphosphonic Acid), Inhibits Bone Resorption As A Sodium Salt And Complexed With Technetium Tc 99m For Bone Imaging. Monophosphonates Are Not Active. Biphosphonates Are Used In Disorders Affecting The Skeleton Such As Osteoporosis, Metastatic Disease And Paget's Disease. While Bisphosphonates Are Analogues Of Endogenous Pyrophosphate Structurally, They Are Characterized By A P-c-p Bond, The Linking Oxygen Is Replaced With A Carbon, Which Is Resistant To Enzymatic And Chemical Hydrolysis. It Is Used For The Treatment Of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis In Women By Building Healthy Bone And Restoring Some Of The Bone Loss As A Result Of Osteoporosis Include Vitamin D And Calcium Supplements.
Details
Molecular Structure